Introduction
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening condition that can strike hard and fast. This severe form of lung injury demands immediate attention. Acute respiratory distress can lead to breathing difficulties and significantly impact one’s health. Recognizing the signs early can be life-saving. This blog aims to break down everything you need to know about ARDS. Understanding ARDS is essential for patients and their families, empowering them to identify issues and seek timely help.
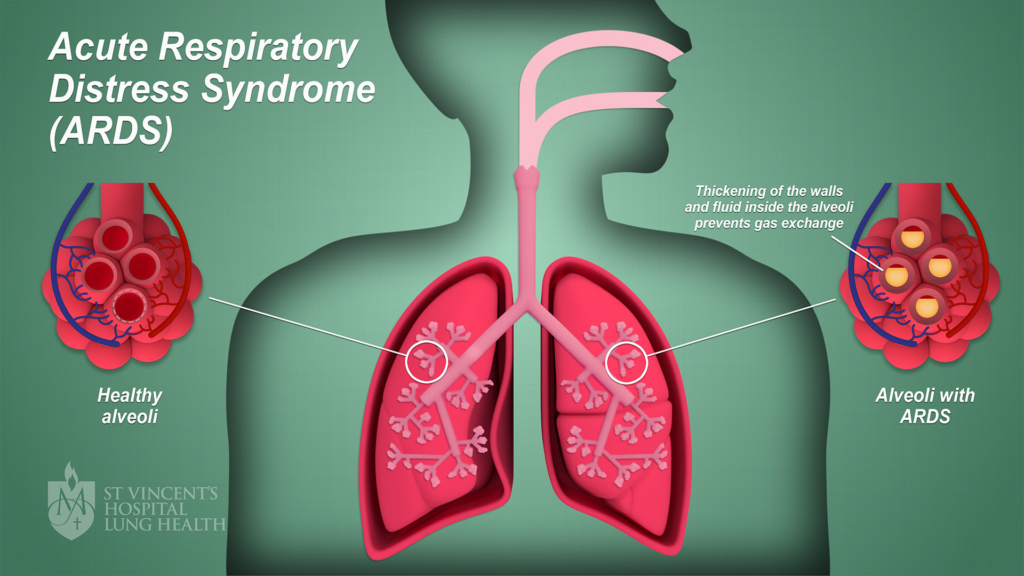
Decoding ARDS: A Closer Look
ARDS occurs when fluid leaks into the lung’s air sacs, making breathing difficult. This fluid buildup is often due to damage in the tiny membranes around these air sacs, called alveoli. The damage can limit oxygen intake, leading to acute respiratory distress. In critical cases, this condition can escalate rapidly, especially in those who are seriously ill. Knowing what ARDS means can help in seeking prompt medical care.
Spotting the Triggers: Common Causes of ARDS
Several acute respiratory distress causes can trigger this condition. Direct causes include pneumonia or inhaling harmful substances like smoke. Indirect causes might be larger systemic issues like severe infections elsewhere in the body. A person could breathe in toxic fumes or battle with septic shock resulting from an infection. Understanding these triggers can help in pinpointing potential acute respiratory distress causes and facilitate better prevention.
Recognizing ARDS: Key Symptoms to Watch For
Watch for these primary symptoms: – Severe shortness of breath – Rapid, labored breathing
Other symptoms may include cyanosis, where the skin turns bluish due to low oxygen. The sudden onset of these symptoms highlights the severity and does not afford any delay. Recognizing these signs promptly is key in tackling ARDS. With early detection, faster intervention is possible.
Demystifying Diagnosis: How Healthcare Professionals Identify ARDS
To diagnose ARDS, healthcare professionals may recommend chest X-rays or blood tests. These tests help identify how much oxygen is in your blood. Common procedures include: – Blood tests – Imaging tests (like X-rays)
Medical teams often combine these diagnostic tools with continuous monitoring to effectively manage and treat Acute Respiratory Distress.
Road to Recovery: Treatment and Long Term Perspectives
Treatment often involves supportive care such as mechanical ventilation to assist with breathing. Recovery time can vary, with some people requiring extended care. Knowing stories of recovery can bring hope to those affected. Many have reclaimed their lives after ARDS with comprehensive treatments and family support.
Empowering with Prevention: Risk Reduction Tips
Reducing risks of ARDS involves: – Treating infections promptly – Avoiding exposure to harmful substances
Especially for vulnerable groups, these proactive approaches can significantly help. Recognizing when to seek immediate medical intervention can make all the difference.
Finding Support: Resources for Patients and Families
Coping with an ARDS diagnosis can be challenging. Support groups and online resources can offer assistance and comfort. Patients should feel encouraged to ask their healthcare providers important questions. This engagement can help in navigating their journey.
Conclusion: Embracing Hope and Awareness
In conclusion, recognizing ARDS early is essential. Swift intervention can positively alter outcomes. We must remain hopeful as ongoing research and advancements continue to improve treatment options. By staying informed about Acute Respiratory Distress and its causes, patients and their families can foster awareness and a hopeful outlook.